Aang_The_last_airbender
First Class Player
- Joined
- Jun 8, 2024
- Runs
- 2,628
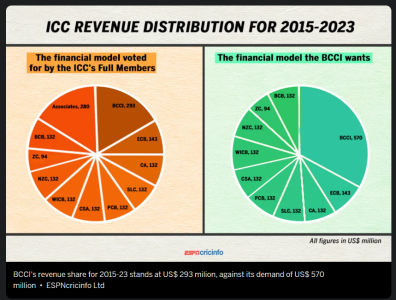
It was a historical spanking BCCI received in 2017 when it got outvoted by EVERY OTHER member of ICC voted unanimously 9-1, when the demanded a higher share which was about 33% of ICC share and got only17% share for the 2015-23 cycle.
----------------
It started with money, and it has ended with money. The "Big Three" financial model drawn up by the boards of India, England and Australia unveiled amid much consternation three years ago is no more, replaced by a plan to vastly reduce the BCCI's share of ICC revenue and offer identical amounts to seven of the game's Full Member nations.
After a week of intense negotiations that saw the BCCI's opposition to change outmaneuvered by the collective will of the rest, the amount of ICC revenue to be handed out to each nation is now as follows. The BCCI will receive US$293m across the eight-year cycle, the ECB US$143m, Zimbabwe Cricket US$94m and the remaining seven Full Members US$132m each. Associate Members will receive total funding of US$280m.
While this distribution is not a complete rollback to the equal funding from ICC events that Full Members used to receive, it is a considerable distance from the US$440 million the BCCI stood to earn under the Big Three model. The distribution to the ECB has reduced marginally from around $US150 million, while Cricket Australia's share is similar to what it previously received, albeit now in line with those afforded to South Africa, Pakistan, New Zealand, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and West Indies. These changes were passed by 14 votes to one, with the BCCI the sole dissenter.
Battles over the ICC events financial model have been drawn out over a period of years, starting with the ascension of Shashank Manohar as the governing body's chairman following the exit of his predecessor and rival N Srinivasan, widely considered the Big Three's chief architect. Manohar stunned the cricket world by stating his intent to resign earlier this year, but was cajoled into staying on until the ICC annual conference in June, where the above changes are set to be ratified.
"This is another step forward for world cricket and I look forward to concluding the work at the Annual Conference," Manohar stated in an ICC release. "I am confident we can provide a strong foundation for the sport to grow and improve globally in the future through the adoption of the revised financial model and governance structure."
The governance structure of which Manohar spoke was the other major outcome from this week's round of meetings in Dubai. The ICC's constitution is to be extensively redrawn, with numerous changes to the way the global game is run and the way that the performance and eligibility of member nations are assessed. These constitutional changes, which were passed by 12 votes to two, include:
More promising was an acknowledgement by the BCCI that it will reconsider its longstanding opposition to cricket's inclusion in the Olympics, a move that other members of the ICC Chief Executives Committee are strongly in favour of pursuing. There was also further discussion of efforts to return international cricket to Pakistan after a gap of eight years. The ICC's chief executive David Richardson was grateful for the amount of progress made.
"It has been a very productive week," he said. "Progress has been made on a number of significant issues, in particular around international cricket structures. Efforts to find a solution, enhancing the context of international bilateral cricket and retaining the relevance of the international game, will continue."
Reaction to the game's new landscape is likely to be varied, much as the Big Three model resulted in heated discussion around the world. In particular, the world awaits the BCCI's response with interest.

 www.espncricinfo.com
www.espncricinfo.com
7 years later,

 www.firstpost.com
www.firstpost.com
BCCI are expected to earn a colossal USD $231 million per year out of ICC’s projected annual earnings of USD $600 million from the 2024-27 cycle. For perspective, the ECB, will take home USD $41.33 million per year (6.89 per cent of the total ICC earnings – less than a fifth of the BCCI), and they are next on the list. Cricket Australia follow next, taking a share of USD $37.5 million – 6.25 per cent. With USD $34.51 million (5.75 per cent), the Pakistan Cricket Board come next. At the other end of the spectrum among the 12 Full Members is Zimbabwe Cricket, at a paltry USD $17.64 million (2.94 per cent). Though they will not fare better than the Associates. The 96 Associate Nations, will earn USD $67.16 million between them – in other words, about USD $700,000 each, or slightly more than a sixtieth of the BCCI’s projected revenue.
BCCI wanted 33% of the ICC share 7 years ago but was rejected by everyone. But 7 years later, it managed to get approval for nearly 40% revenue share. What caused this change ?
----------------
It started with money, and it has ended with money. The "Big Three" financial model drawn up by the boards of India, England and Australia unveiled amid much consternation three years ago is no more, replaced by a plan to vastly reduce the BCCI's share of ICC revenue and offer identical amounts to seven of the game's Full Member nations.
After a week of intense negotiations that saw the BCCI's opposition to change outmaneuvered by the collective will of the rest, the amount of ICC revenue to be handed out to each nation is now as follows. The BCCI will receive US$293m across the eight-year cycle, the ECB US$143m, Zimbabwe Cricket US$94m and the remaining seven Full Members US$132m each. Associate Members will receive total funding of US$280m.
While this distribution is not a complete rollback to the equal funding from ICC events that Full Members used to receive, it is a considerable distance from the US$440 million the BCCI stood to earn under the Big Three model. The distribution to the ECB has reduced marginally from around $US150 million, while Cricket Australia's share is similar to what it previously received, albeit now in line with those afforded to South Africa, Pakistan, New Zealand, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and West Indies. These changes were passed by 14 votes to one, with the BCCI the sole dissenter.
Battles over the ICC events financial model have been drawn out over a period of years, starting with the ascension of Shashank Manohar as the governing body's chairman following the exit of his predecessor and rival N Srinivasan, widely considered the Big Three's chief architect. Manohar stunned the cricket world by stating his intent to resign earlier this year, but was cajoled into staying on until the ICC annual conference in June, where the above changes are set to be ratified.
"This is another step forward for world cricket and I look forward to concluding the work at the Annual Conference," Manohar stated in an ICC release. "I am confident we can provide a strong foundation for the sport to grow and improve globally in the future through the adoption of the revised financial model and governance structure."
The governance structure of which Manohar spoke was the other major outcome from this week's round of meetings in Dubai. The ICC's constitution is to be extensively redrawn, with numerous changes to the way the global game is run and the way that the performance and eligibility of member nations are assessed. These constitutional changes, which were passed by 12 votes to two, include:
- Opening a pathway to include additional Full Members in the future subject to meeting membership criteria
- Removing the Affiliate level of membership so there are only two levels; Full Member and Associate Member
- Introducing an independent female director to the board
- Introducing membership criteria and forming a Membership Committee to consider membership applications
- Introducing a deputy chairman of the board who will be a sitting director elected by the board to stand in for the chairman in the event that he or she is unable to fulfil their duties
- Equally weighting votes for all board members regardless of membership status
- Entitling all members to attend the Annual General Meeting
More promising was an acknowledgement by the BCCI that it will reconsider its longstanding opposition to cricket's inclusion in the Olympics, a move that other members of the ICC Chief Executives Committee are strongly in favour of pursuing. There was also further discussion of efforts to return international cricket to Pakistan after a gap of eight years. The ICC's chief executive David Richardson was grateful for the amount of progress made.
"It has been a very productive week," he said. "Progress has been made on a number of significant issues, in particular around international cricket structures. Efforts to find a solution, enhancing the context of international bilateral cricket and retaining the relevance of the international game, will continue."
Reaction to the game's new landscape is likely to be varied, much as the Big Three model resulted in heated discussion around the world. In particular, the world awaits the BCCI's response with interest.

New ICC finance model breaks up Big Three
During the ICC meetings over the week in Dubai, intense negotiations saw the BCCI's opposition to change outmaneuvered by the collective will of the rest

7 years later,

BCCI to receive 38.5% share in ICC's new revenue model for 2024-27 cycle
The BCCI will get 38.4 per cent of the share; at least six times more than the distant second and third on the list: England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB) and Cricket Australia (CA), who will get around 6.89 and 6.25 per cent respectively
BCCI are expected to earn a colossal USD $231 million per year out of ICC’s projected annual earnings of USD $600 million from the 2024-27 cycle. For perspective, the ECB, will take home USD $41.33 million per year (6.89 per cent of the total ICC earnings – less than a fifth of the BCCI), and they are next on the list. Cricket Australia follow next, taking a share of USD $37.5 million – 6.25 per cent. With USD $34.51 million (5.75 per cent), the Pakistan Cricket Board come next. At the other end of the spectrum among the 12 Full Members is Zimbabwe Cricket, at a paltry USD $17.64 million (2.94 per cent). Though they will not fare better than the Associates. The 96 Associate Nations, will earn USD $67.16 million between them – in other words, about USD $700,000 each, or slightly more than a sixtieth of the BCCI’s projected revenue.
BCCI wanted 33% of the ICC share 7 years ago but was rejected by everyone. But 7 years later, it managed to get approval for nearly 40% revenue share. What caused this change ?
Last edited by a moderator:






